BrainBot Collision
The BrainBot is equipped with a distance sensor. You can use the distance sensor to determine how far away something is and then program the robot to avoid it.
Prerequiste
This lesson assumes you’ve already assembled the BrainBot & read the intro, BrainBot API and made the BrainBot Dance.
Remember you’ll also need to add the BrainBot NuGet if you’re programming in C#. MicroPython has it built in, so you’ll just need to add the import statement.
using static BrainPad.Controller;
using static BrainPad.BrainBot;from BrainPad import *
from BrainBot import *Distance Sensor
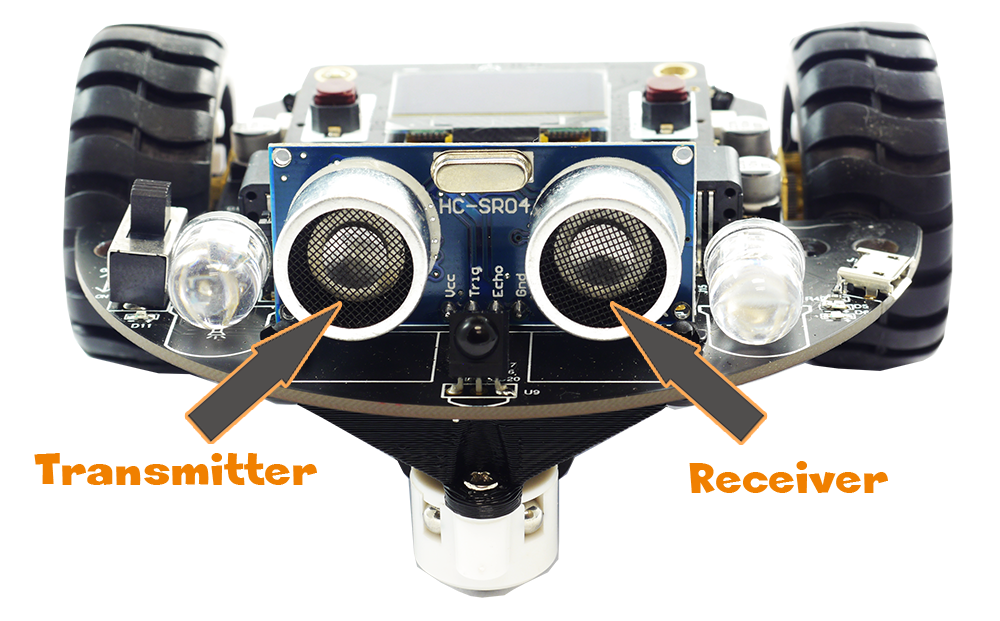
The distance sensor on the BrainBot looks like the two eyes at the front. These ‘eyes’ are what are used to transmit and receive the echo that bounces off object that it comes near. One of the ‘eyes’ is the Transmitter and the other is the Receiver.
If you’d like to know more about how distance sensors work, check out the Distance lesson.
Reading Distance
while(true){
var distance = DistanceSensor();
Print (distance);
}while True:
distance = DistanceSensor()
Print(distance)
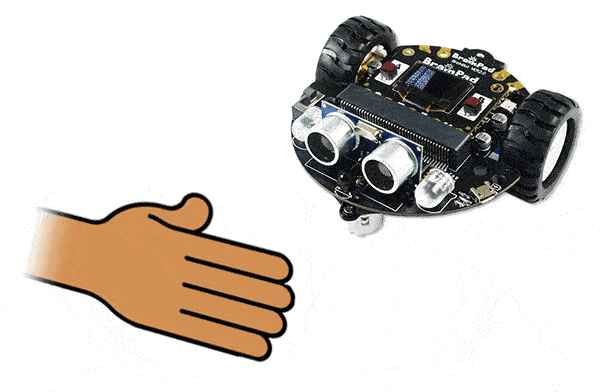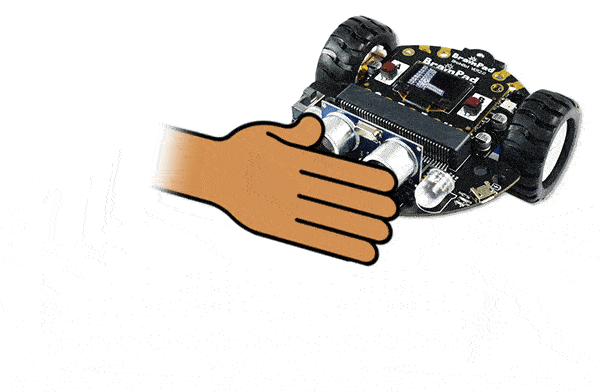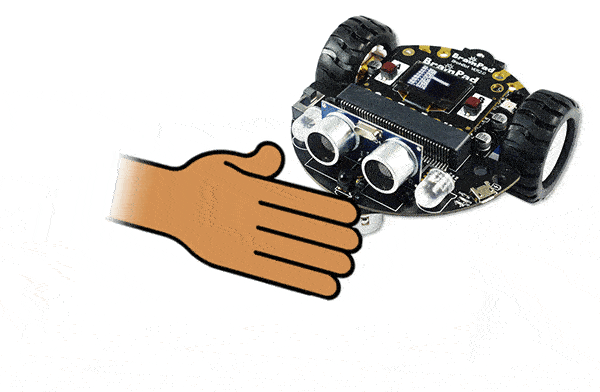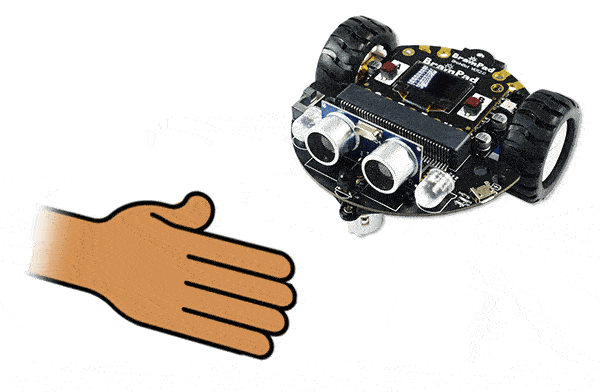
When you run the program, try putting your hand close to the sensors and then pull your hand further away. You’ll notice the value changing as you move your hand. This is now reading the distance.
Avoiding Obstacles
First, create a function to handle what the BrainBot does when it’s less than 25 centimeters from an object. Call the function you create TurnAround().
void TurnAround(){
Stop();
Move(-40,-40);
Wait(0.2);
Move(40, -40);
Wait(0.2);
}
def TurnAround():
Stop()
Move(-40,-40)
Wait(0.2)
Move(40, -40)
Wait(0.2)
Since we’re going to move the BrainBot, add a button to start the process so the BrainBot doesn’t run away when we’re testing it.
You can use the distance variable you created to make the BrainBot back up and turn around when it gets under 25 centimeters away from an object.
void TurnAround(){
Stop();
Move(-40,-40);
Wait(2);
Move(40, -40);
Wait(0.1);
}
//Wait for Button A press
Print("Press A to Start");
var btnA = Button(ButtonA, 0);
while(In(btnA) == 0) {
Wait(0.1);
}
while(true){
var distance = DistanceSensor();
Print(distance);
Move(40,40);
if (distance < 25) {
TurnAround();
}
}def TurnAround():
Stop()
Move(-40,-40)
Wait(0.2)
Move(40, -40)
Wait(0.2)
#Wait for Button A press
Print("Press A to Start")
btn = Button(ButtonA, 0)
while In(btnA == 0):
Wait(0.1)
while True:
distance = DistanceSensor()
Print(distance)
Move(40,40)
if distance < 25:
TurnAround()
What’s Next?
Now that you’ve mastered moving the BrainBot around and avoiding obstacles, you can program the BrainBot to follow a specific path in the next BrainBot Autonomous Lesson.
BrainStorm
A distance sensor is what a car would use as a backup sensor. It measures the distance to what is behind and make a sound reflecting that distance. There are no intelligence there, no decision making. Some cars may have control over the breaks system and it will automatically stop the car if it detects an object that is getting too close to the car. In this case we are starting to add some intelligence and decision making.